Right Embryo
A genetic test designed to reduce the risk of having a child with an inherited condition

What is PGT-M?
For people who know they are at increased risk of passing on a specific genetic condition, PGT-M, or preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic/single-gene defects, can be performed prior to embryo transfer to greatly reduce the risk of having a child affected with that condition.
PGT-M for single gene disorders involves testing embryos created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) and then transferring unaffected embryos. PGT-M was formerly known as PGD, preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
How it works
PGT-M tests are created uniquely for each family. PGT-M can be performed for nearly any single-gene disorder as long as the specific familial mutation has been identified and appropriate family members are available for test preparation.
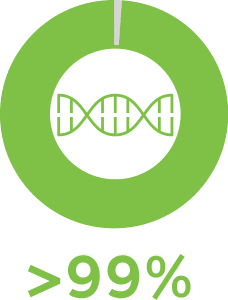
PGT-M can be performed for >99% of inherited single-gene disorders

PGT-M identifies affected and unaffected embryos with >99% accuracy
Who is PGT-M for?
PGT-M is appropriate for people who are at high-risk of passing on a specific single-gene disorder. You may consider PGT-M if:
- You and your partner are carriers of the same autosomal recessive condition (e.g. Cystic fibrosis)
- You are a carrier of an X-linked condition (e.g. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy)
- You or your partner have an autosomal dominant condition (e.g. Huntington disease)
- You or your partner have a mutation associated with a hereditary cancer syndrome (e.g. BRCA1 & 2)
- You had a child or pregnancy with a single gene disorder
- You want to perform HLA matching
The PGT-M Process

Case review
Ordering provider submits a TRF along with genetic testing reports for case review and approval.

Genetic consultation
Registered patients speak with a genetic counselor
(PGT-M: discuss if additional genetic testing of the couple or other family members is required).

PGT-M process
PGT lab collects DNA samples from the couple and appropriate family members and designs a test unique to each family.

IVF
In vitro fertilization is performed and the resulting embryos are incubated.

Embryo biopsy
An embryologist carefully removes a small cell sample from each embryo.

Vitrification
Embryos are frozen while awaiting PGT results.

PGT-M
Biopsied samples are sent to the PGT laboratory, testing is performed, and results are released to the IVF center.

Embryo transfer
If available, a chromosomally normal embryo is selected for transfer. Additional euploid embryos can remain frozen for future use.
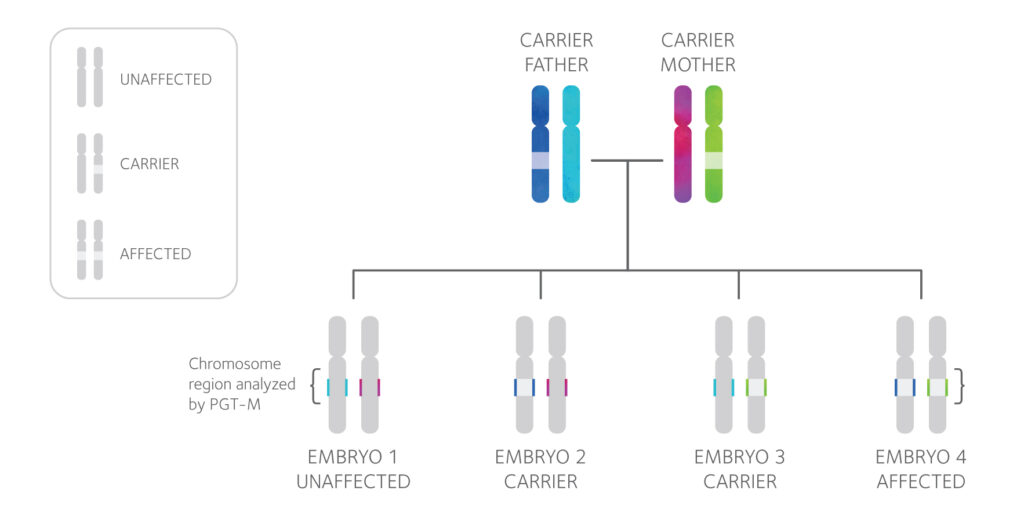
PGT-M Technology
PGT-M testing involves a close examination of both the mutation an individual carries and the area of the chromosome surrounding it, shown above as the colored segment of each chromosome.
Each PGT-M test design is unique and specific to the family, so DNA samples from both partners, and often additional family members, will be requested in order to design a test.
Then, linkage analysis is used to determine the “genetic fingerprint” of the mutation and diagnose each tested embryo as affected or unaffected.
PGT-M/SR Experience
CooperSurgical is the pioneer and worldwide leader of PGT-M/SR. Our experts have over a 100 years of combined PGT-M experience and global expertise in providing accurate results – highlighted by our ability to accept the most complex of cases.
